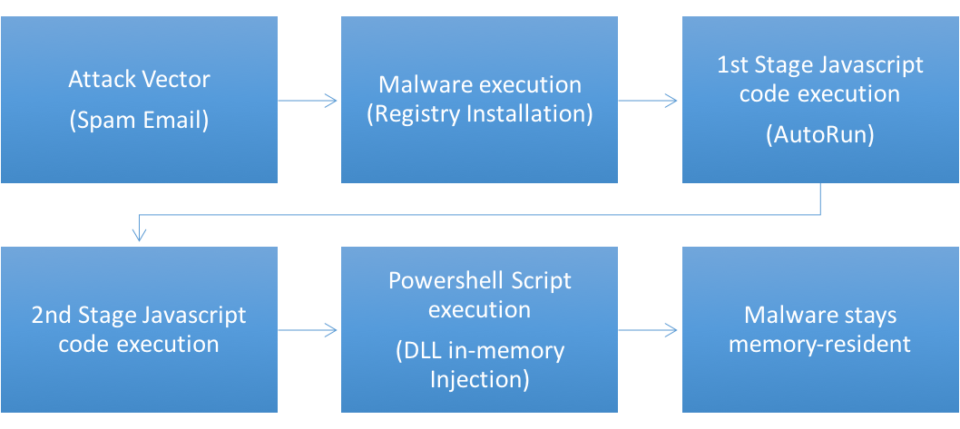
Discovered by security giants Kaspersky, who also gave the malware its name, SessionManager appears to have been at large since March 2021, but its existence has only just been confirmed. It’s believed that SessionManager was created by Gelsemium, a relatively new hacking group who have already conducted a number of serious cyber-attacks.
Naturally, you would expect military and government organizations to have some of the strongest cybersecurity measures in place. And they do. However, there’s not a single IT infrastructure which can be described as 100% secure. And, as SessionManager has proved, where there are vulnerabilities, there’s a way in.
How Does SessionManager Operate?
At the start of 2021, Kaspersky revealed details of ProxyLogon, a series of vulnerabilities discovered in Microsoft Exchange. As a result of these vulnerabilities, threat actors were presented with an opportunity to install malicious modules into web server software for Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS). And this is exactly how the SessionManager module came to be embedded within numerous organization’s servers.
Once installed, the threat actors were able to use SessionManager to carry out the following tasks:
- Carry out remote command execution on affected devices
- Gain quick and easy access to email accounts within the organization
- Install further malware to maximize the way in which servers were compromised
- Using infected servers to manipulate traffic moving across the network
As SessionManager has managed to operate without detection for over a year, it has been able to harvest signification amounts of sensitive data and take control of high-level networks. Even after SessionManager’s discovery, security experts have been slow to move, with Kaspersky commenting that a popular file scanning service was still failing to detect SessionManager. Accordingly, SessionManager remains active in the digital wild and maintains its threat.
What If You’re Infected with SessionManager?
Even if you do discover that your network has been infected by the SessionManager module, deleting it is not enough to fully rid yourself of it. Instead, you will need to go through the following:
- The most important step to take first is to disable your IIS environment
- Use the IIS manager to identify all references to the SessionManager module and ensure that these are fully removed
- Update your IIS server to eliminate any known vulnerabilities and leave it fully patched
- Restart your IIS environment and run a final check for any traces of SessionManager
If, of course, you want to prevent vulnerability threats such as SessionManager being enabled in the first place, then you need a conscientious approach to updates. The sooner you can install a firmware upgrade or a security patch, the sooner you can plug security holes in your IT infrastructure.
Sure, we live in a fast-paced world and it’s easy to forget minor tasks such as installing upgrades, but with automate installs a viable option, there’s not really an excuse. Therefore, keep your organization’s network safe by automating updates and enjoying the peace of mind this brings.
For more ways to secure and optimize your business technology, contact your local IT professionals.
Read More